Your cat’s eyes, which are usually bright and clear, have started to look watery and irritated. You might notice them pawing at their eyes or rubbing their face on the furniture more than usual. These are signs that something could be wrong.
In this article, Nexus-Pets will help you understand common cat eye problems their causes, symptoms, and effective treatments to keep your furry friend comfortable and healthy.
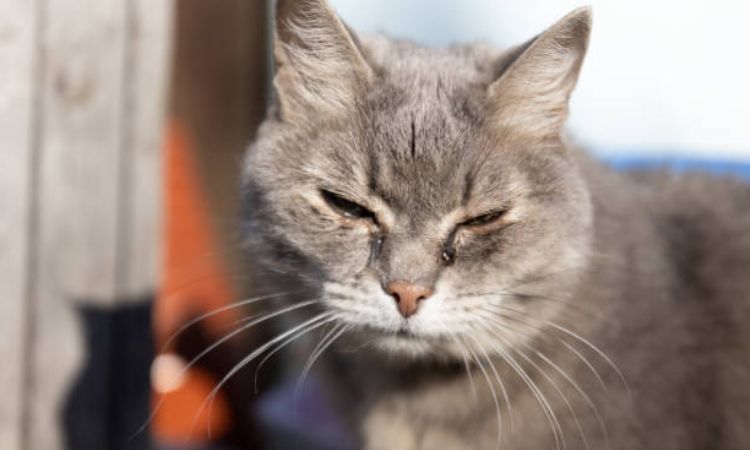

Common Causes of Cat Eye Problems
Cats can develop eye issues due to a wide range of factors, from infections and environmental irritants to trauma and systemic health conditions. Understanding these causes helps in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate care.
Some of the most frequent causes include:
- Infections: Viral, bacterial, and fungal agents can affect the eyes.
- Feline herpesvirus (FHV-1) is a common viral cause leading to inflammation and discharge.
- Chlamydia and calicivirus also contribute to eye and respiratory problems.
- Allergies and Environmental Irritants: Exposure to pollen, dust, cigarette smoke, or harsh chemicals often triggers redness, watering, and itching.
- Trauma and Injuries: Scratches from claws, foreign bodies lodged in the eye, or blunt impacts can damage eye tissues, causing pain and inflammation.
- Immune-Mediated Diseases: These conditions cause the immune system to mistakenly attack parts of the eye, leading to chronic inflammation.
- Age-Related Conditions: As cats grow older, changes in eye structure and function may result in vision difficulties.
- Other Underlying Health Issues: Systemic diseases like diabetes and hypertension can impair eye health and contribute to various ocular complications.
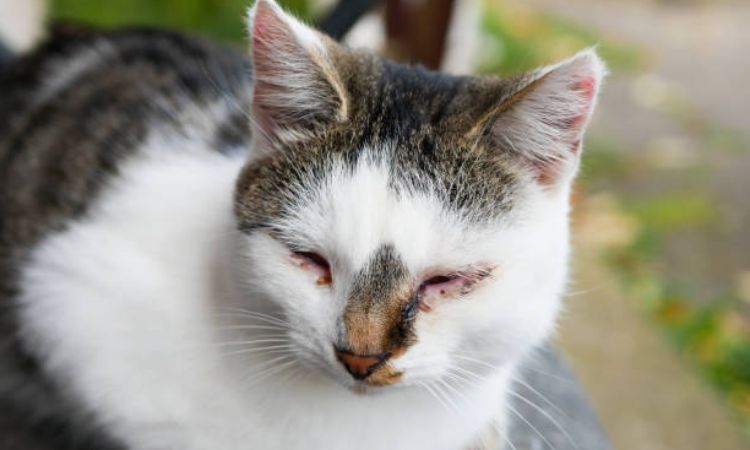

Common Cat Eye Problems and Their Symptoms
Cats can experience a variety of eye issues, each presenting with distinct symptoms. Recognizing these signs early can help ensure timely veterinary care and prevent complications.
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
This condition is characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane covering the white part of the eye and inner eyelids. Typical symptoms include redness, swelling around the eye, watery or thick discharge, and frequent squinting due to discomfort.
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Triggered by allergens such as pollen, dust, or chemicals, allergic conjunctivitis causes the eyes to become red, itchy, and watery. Cats may excessively rub their eyes, leading to further irritation.
Uveitis (Inflammation of the Uveal Tract)
Uveitis involves inflammation of the middle layer of the eye (uvea) and is often painful. Symptoms include a bloodshot or red eye, sensitivity to light, and a hazy or cloudy appearance of the eye’s surface.
Keratitis (Corneal Inflammation)
Inflammation of the cornea presents with eye cloudiness, redness, discharge, and noticeable discomfort or pain. Cats may blink excessively or avoid bright light.
Corneal Ulcers
These are open sores or scratches on the cornea. Cats with corneal ulcers often show signs of eye pain, including squinting, excessive blinking or tearing, and discharge. Prompt treatment is essential to avoid worsening or infection.
Entropion (Inward Rolling of Eyelids)
Entropion causes the eyelids to roll inward, making the eyelashes rub against the cornea. This leads to redness, squinting, a cloudy cornea, and frequent eye rubbing. It can be painful and may result in corneal damage if untreated.
Cataracts
Cataracts develop when the lens inside the eye becomes cloudy, impairing vision. Affected cats may show a cloudy or whitish pupil and exhibit signs of vision loss, such as bumping into objects or reluctance to move in unfamiliar areas.
Dry Eye (Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca)
Dry eye occurs when tear production is insufficient, leading to inflammation and irritation. Symptoms include red eyes, a sticky yellow discharge, and general eye discomfort. If left untreated, dry eye can cause corneal ulcers or scarring.
Eye Injuries and Trauma
Physical injuries to the eye, such as scratches, blunt force, or foreign bodies, often result in swelling, bleeding, and pain. Severe trauma may put the cat at risk of permanent vision loss or blindness, making immediate veterinary attention crucial.
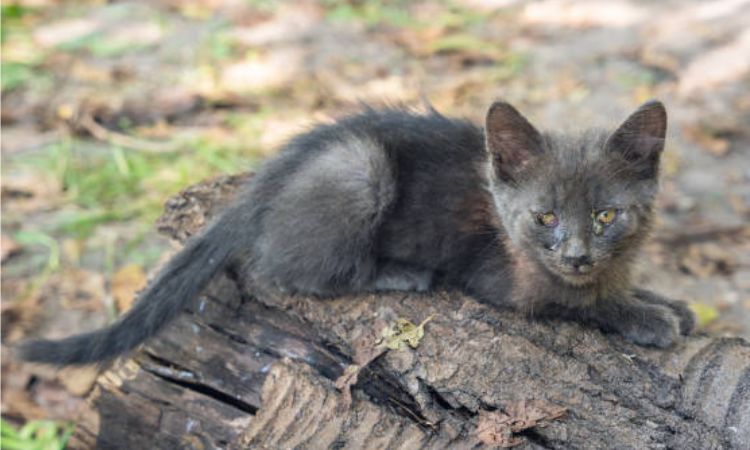

Diagnostic Approaches
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to effectively treat eye issues in cats. When your cat shows signs of eye discomfort or abnormality, a thorough veterinary eye examination is the first essential step. This examination typically involves a detailed inspection of the eye structures using specialized tools to assess the cornea, conjunctiva, eyelids, and internal eye components.
Several diagnostic tests help pinpoint the exact nature and cause of the eye problem:
- Fluorescein Stain Test: This test involves placing a special dye on the surface of the eye to detect corneal ulcers, scratches, or foreign bodies. Areas of corneal damage will absorb the dye and fluoresce under a blue light, making them easy to identify.
- Tear Production Measurement (Schirmer Tear Test): Measuring tear production helps diagnose conditions like dry eye (keratoconjunctivitis sicca). A small strip of paper is placed under the lower eyelid to assess how much moisture the eye produces over a short period.
- Microbial Cultures and Cytology: When infections are suspected, samples of eye discharge or tissue may be collected to identify bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogens. This allows for targeted treatment based on the specific infectious agent.
To uncover underlying causes, especially in recurrent or severe cases, veterinarians may recommend additional laboratory tests or imaging studies. Blood tests can reveal systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, or immune disorders that contribute to eye conditions. Imaging techniques like ultrasound or advanced ocular scans help evaluate internal eye structures and detect issues such as retinal detachment, glaucoma, or tumors.
Effective Treatments for Cat Eye Problems
Treating eye conditions in cats requires a tailored approach depending on the underlying cause and severity. A combination of medications, home care, and sometimes surgical intervention can help restore eye health and prevent complications.
Medications
- Antibiotics (Topical and Oral): Used to combat bacterial infections affecting the eye, including conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, and secondary infections. Topical ointments or eye drops are often prescribed for localized treatment, while oral antibiotics may be necessary for more severe or systemic infections.
- Antiviral Drugs: Essential for managing viral infections such as feline herpesvirus (FHV-1), which commonly causes recurrent eye inflammation and discharge. Antiviral medications help reduce viral activity and symptoms.
- Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Both corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to reduce inflammation and swelling. Steroids are effective in controlling conditions like uveitis and allergic conjunctivitis but must be used cautiously under veterinary supervision due to potential side effects.
- Antihistamines: Prescribed to alleviate symptoms related to allergies, including itchy, watery eyes and conjunctival inflammation caused by environmental irritants such as pollen, dust, or smoke.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: For immune-mediated eye diseases, such as immune-related uveitis or keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eye), immunosuppressants help reduce immune system overactivity that damages eye tissues.
Eye Care at Home
- Cleaning Discharge Safely: Gently wiping away eye discharge with a clean, damp cotton ball or cloth helps maintain hygiene and prevents further irritation. Always wipe from the inner corner outward, using a fresh cloth for each eye.
- Avoiding Irritants: Minimizing exposure to smoke, dust, harsh chemicals, or allergens reduces inflammation and prevents worsening of symptoms.
- Providing a Calm Environment: Dimming lights and providing a quiet space helps ease discomfort, especially for cats with light sensitivity due to uveitis or corneal issues.
Surgical Options
Certain eye problems may require surgical intervention for a successful outcome:
- Cataract Surgery: In cases of significant vision impairment due to lens clouding, surgery can restore sight.
- Entropion Correction: Surgical repair is needed to correct inward-rolling eyelids that cause corneal damage and pain.
- Treatment of Severe Ulcers or Trauma: Surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue, repair corneal ulcers, or address traumatic injuries to prevent permanent vision loss.
Pain Management and Supportive Care
Pain relief is crucial for cats experiencing eye discomfort. Veterinarians may prescribe analgesics alongside other treatments to ensure your cat remains comfortable during recovery. Supportive care, including hydration and nutritional support, can also aid healing.
Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up visits to the veterinarian are important to assess treatment effectiveness and adjust care as needed. Early detection of complications or recurrence improves prognosis and preserves your cat’s vision and quality of life.
Staying alert to the diverse causes and subtle symptoms of feline eye problems is crucial. Thankfully, a range of effective treatments can restore comfort and clarity to your cat’s vision. Swift action and veterinary consultation ensure optimal eye health and well-being for your beloved companion.